
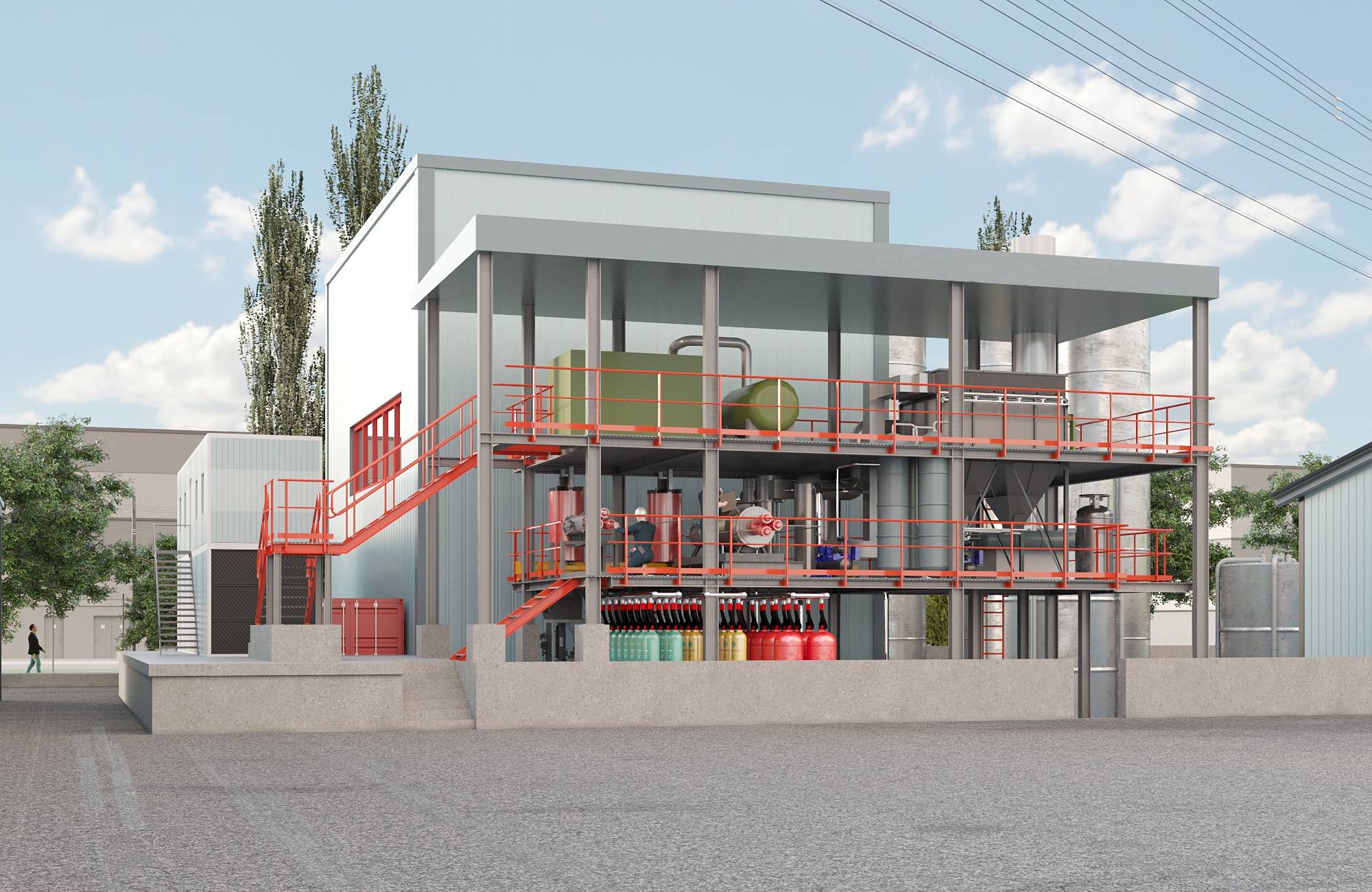
envirotech agency
Advanced solutions such as plasma processing and material recovery optimize resource use and support circular economy principles. These technologies help businesses achieve environmental goals and contribute to a greener future.
"Transforming Waste into Value"

Advanced solutions such as plasma processing and material recovery optimize resource use and support circular economy principles. These technologies help businesses achieve environmental goals and contribute to a greener future.


In some cases, the use of electric energy instead of fuel is cheaper, especially forplasmatrons of industrial frequency, due to the availability of a wide range of standard equipment of this type in the market. In case of autonomous installations of small capacity, the choice of electric energy eliminates the problems of delivery, storage and supply of fuel and improves the safety of the combustion process.
PLASMA: In natural conditions, plasma is formed, for example, when earth's atmosphere is ionized by electric discharge, forming lightnings. A plasma essentially represents a gas heated to very high temperatures, in which the processes of dissociation (the decay of molecules into atoms) and ionization (the detachment of electrons from the outer electron shells of atoms) is taking place. Since the physical properties of plasma significantly differ from those of of gases, it is customary to call it the fourth state of aggregation of matter.
The high temperature characteristic for a plasma provides some distinct key advantage over traditional, lowertemperature, combustion-based thermal processes.
Traditionally, plasma is produced using special devices – plasmatrons. As a result of heat exchange, the carrier gas heats up to high temperatures. The resulting plasma can then be used to drive downstream equipment, such as gasification reactors.
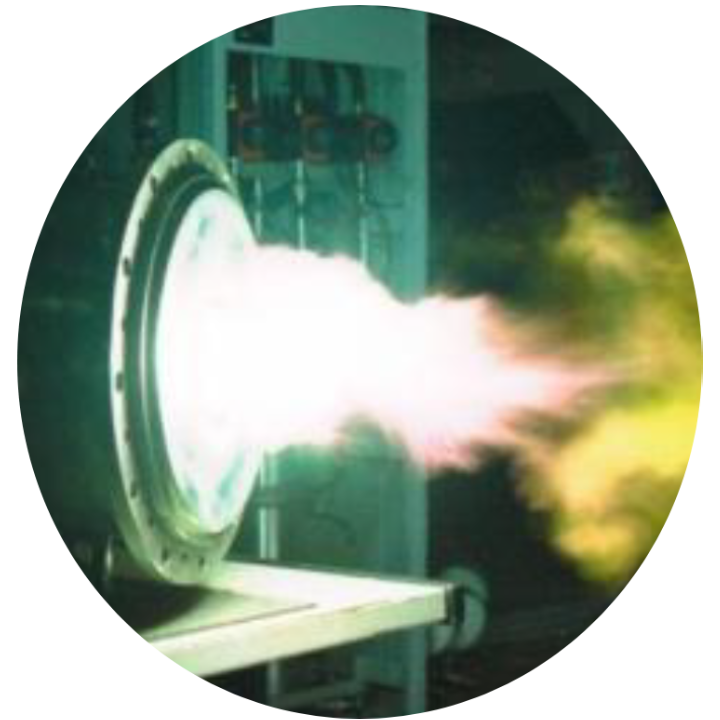


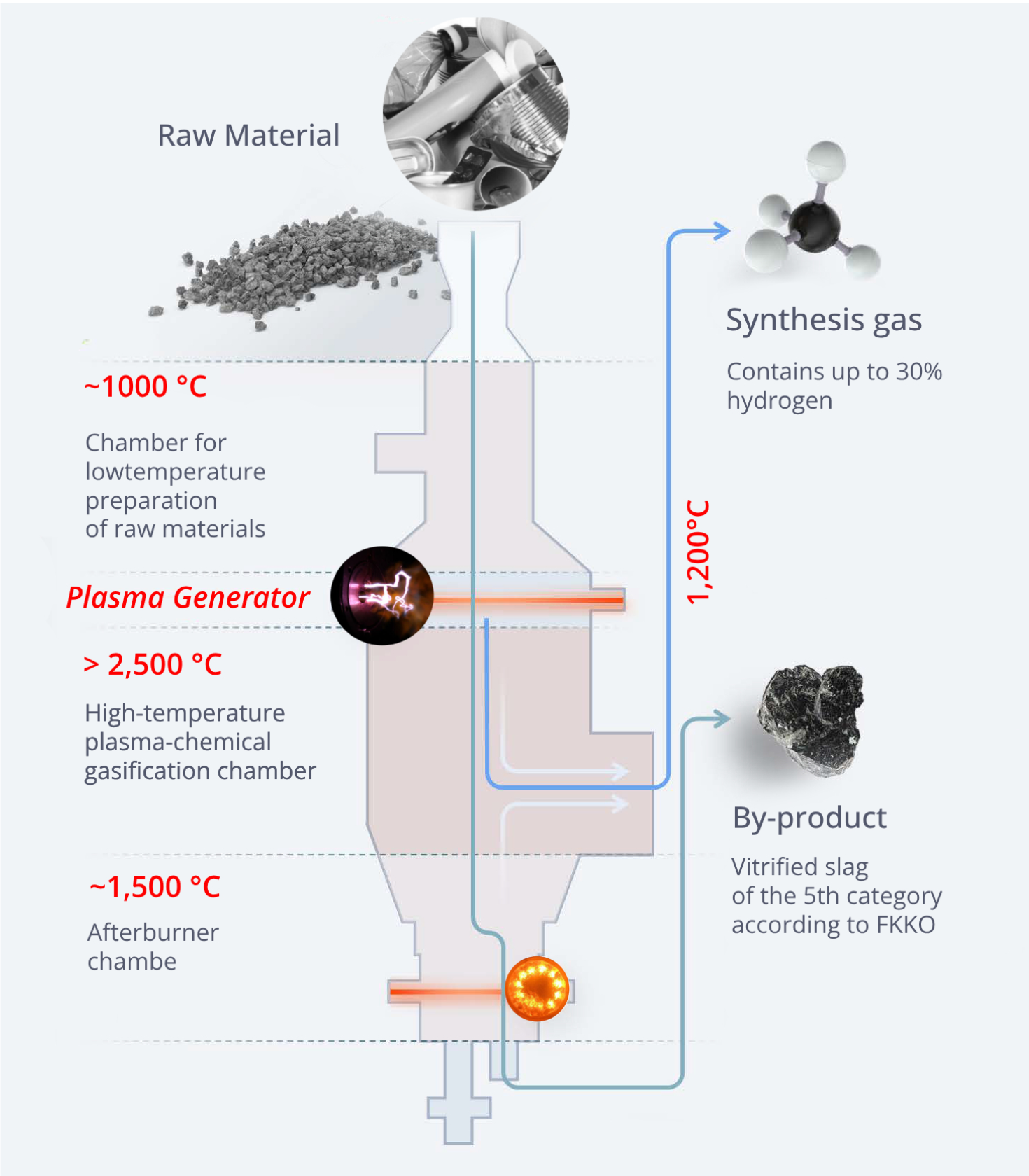
PLASMA GASIFIER / GASIFICATION REACTORS
A plasma gasifier consists of a reaction chamber in which the process of plasma gasification occurs. Plasma
gasification is a thermochemical process in which the organic component of some feed material heated by a
plasma jet is decomposed into a gaseous form, forming a combustible gas called syngas, consisting mainly of
carbon monoxide CO and hydrogen H2.
Syngas has a wide range of applications. It, for example, can be converted into ethyl alcohol, methanol, diesel
fuel. Alternatively it can be burned to receive electric and/or thermal energy. Depending on the conditions and
intended use, it requires gas cleaning such as the removal of solid particles, acid gases, heavy metals and other
undesirable elements before further use.
Inorganic constituents of waste such as metal, glass are removed from the bottom of the gasifier in a liquid
molten state. The melt is quenched with water forming a glass-like material , which can be further used, for
example, in civil or road construction.
Our technology is unique, in the sense that it comprises a stand-alone process, which - if the energy for the
plasmatron is produced from the syngas -allows one to completely abandon use of (potentially) expensive
external energy sources. Plasma gasification is a widely applied and proven technology which solves many
problems, maintaining a balance between waste disposal, energy production, reducing emissions of harmful
greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and preserving the environment.
As material for: